DC Motor
1. Learning Outcomes
After completing this Section, you will be able to:
- Explain the principles of DC motor polarity control and demonstrate safe and effective operation of a DC motor under bidirectional drive.
- Design, implement, and validate an H-bridge circuit to achieve bidirectional (polarity-reversing) control of a DC motor.
2. Hardware Set-Up
xxxx
Note that while the ACE-Box can be used for all the exercises, it is not required and only the individual components are needed.
Required hardware for this exercise:
- Supported Arduino Uno board
- H-bridge
- DC gearbox (50:1) 6V motor
- USB cable
- 9V battery
- 9V power jack
- 2 x male-male wires
- 2 x male-female wires
- 2 x male-copper wires
Set-up the hardware as shown and following these steps:
- xxxx
Download Now
Download the PDF version of the exercise
3. Simulink Setup
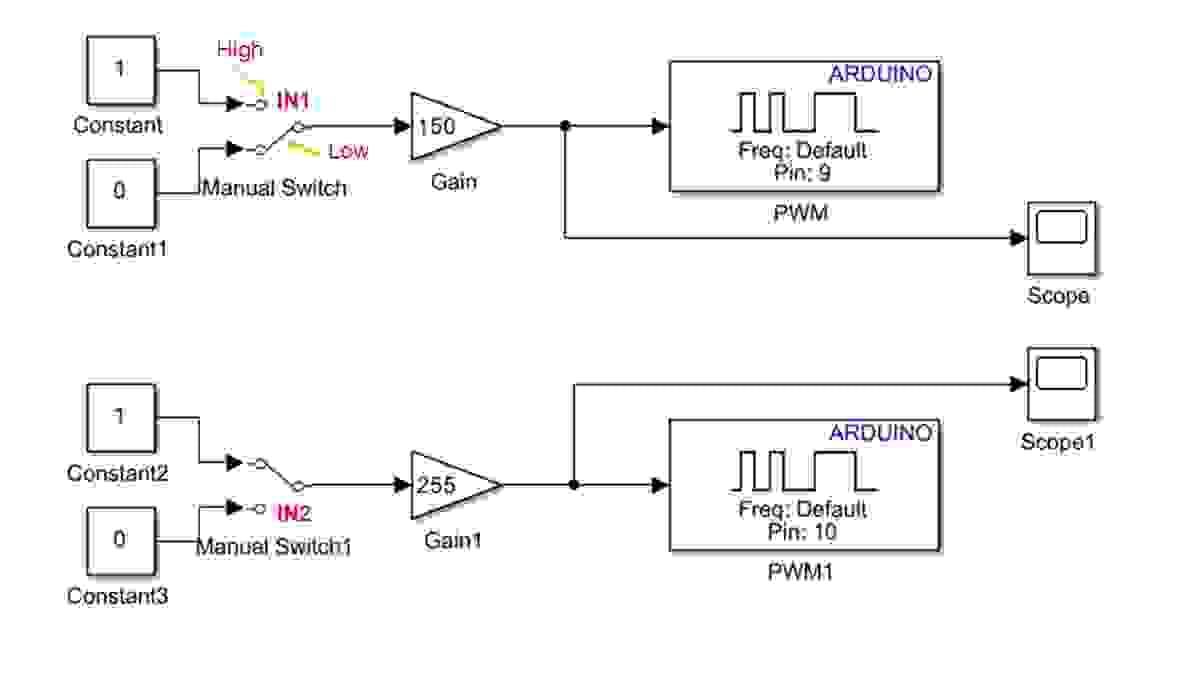
The Simulink block diagram for the H-bridge algorithm design is given, with the logic used for controlling the 'forward' and 'reverse' motion of the DC motor. Please note
that to implement this in real-time on a physical system, the switches would
need to be external, or logic built into Simulink. Based on the electronic circuit set-up
provided above, the operation of the H-bridge polarity ‘control’ operates as
follows:
1. ClockwiseMotion- Set IN1 to High
- Set IN2 to Low
2. CounterclockwiseMotion
- Set IN1 to Low
- Set IN2 to High
3. Stop Motion
- Set both IN1 and IN2 to Low
- Set both IN1 and IN2 to High
Once, set-up and operating withinSimulink, perform the following:
- Changethe switches as detailed above and view the scopes to explore how the signals are changing
- Asthe PWM has values between 0 and 255 (150 and 255 are initially given below),
investigate changing the numbers within the gain blocks to alter the speed of
the DC motor.
Download Now
Download the PDF version of the exercise
Advancing automatic control engineering (ACE) education through global collaboration



