LED (PWM) Exercise
1. Learning Outcomes
After completing this Exercise, you will be able to:
- Understand the use of the Simulink Arduino support package for algorithm design applied to a simple circuit.
- Understand the operation of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) through the control of LED brightness.
After completing this exercise, you are encouraged to review the learning outcomes and confirm that they have been met.
2. Requirements
The exercise has the following primary requirements:
- The Simulink model shall generate a Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) output signal to control the brightness of an LED connected to an Arduino Uno.
- The Simulink model shall vary the PWM duty cycle over the full 8-bit range (0 – 255),where a value of 0 turns the LED fully OFF and a value of 255 turns the LED fully ON.
- The Simulink model shall use a sine wave–based input signal, processed through appropriate blocks, to smoothly vary the LED brightness over time.
- The Simulink model shall drive Arduino PWM-capable digital pin 9 using the PWM block from the Simulink Support Package for Arduino Hardware.
- The Simulink model shall be deployable to an Arduino Uno using Simulink code generation and shall execute continuously in real-time (simulation stop time set to infinity).
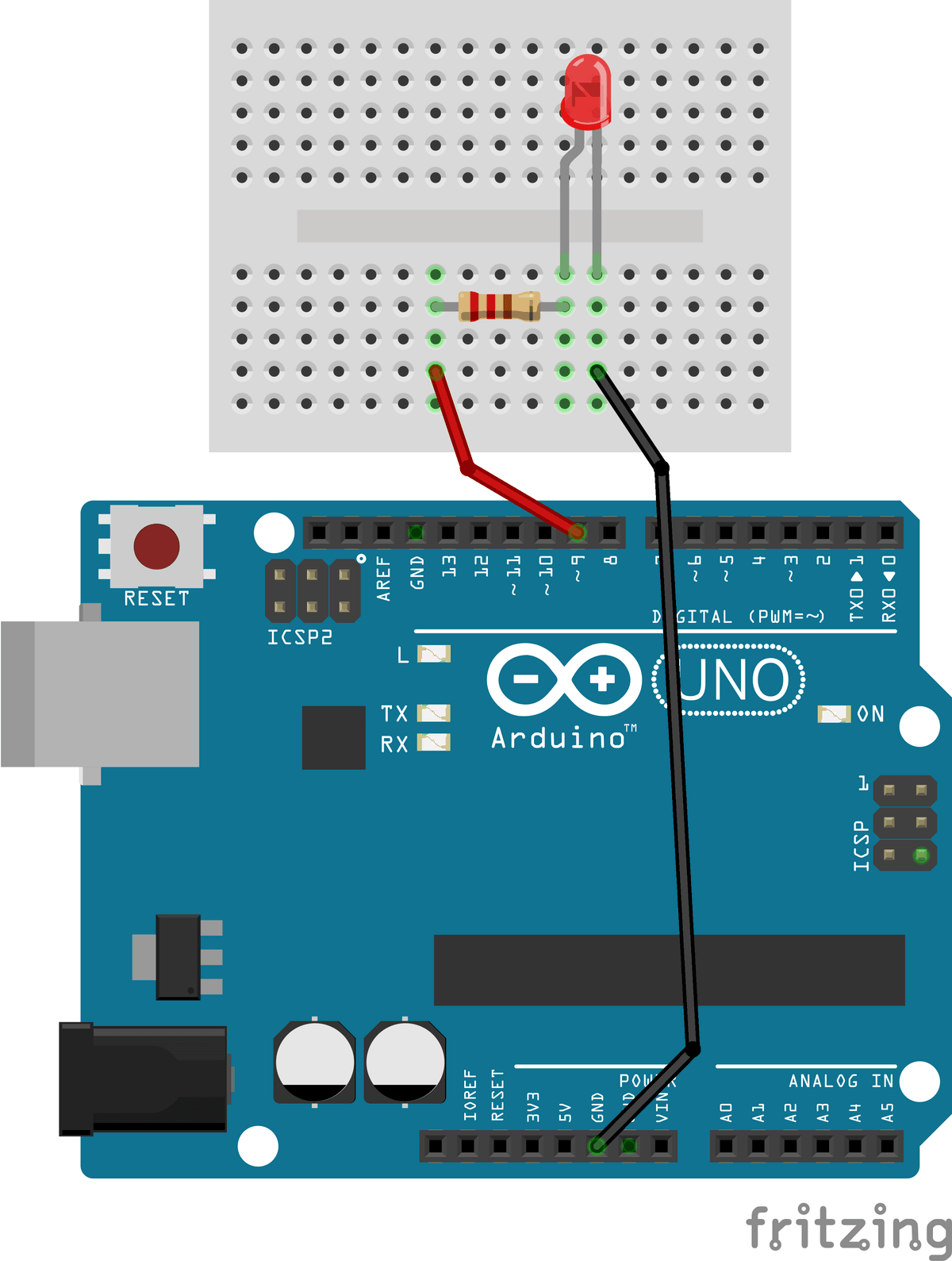
3. Hardware Set-Up
This exercise uses the same hardware configuration as the previous LED (Digital) exercise. Note that there is a video at the end of this Section to aid with your understanding, as shown in Figure 1.
The exercise involves connecting an LED to a PWM-capable Arduino output pin and controlling its brightness using 8-bit PWM resolution, providing 256 discrete brightness levels.
Required hardware for this exercise:- Arduino Uno board (supported by Simulink)
- USB Cable (Type A to Type B)
- Breadboard
- LED
- 220 Ohm resistor
- 2 x male-to-male breadboard wires
HardwareAssembly Steps
- Connect digital pin 9 on the Arduino to a chosen column on the breadboard using a jumper wire.
- Insert a 220 Ω resistor with one end in the same column as the wire from pin 9 and the other end in a different row.
- Insert the LED such that:
- The long leg (anode) connects to the free end of the resistor.
- The short leg (cathode) connects to an Arduino GND pin using a jumper wire.
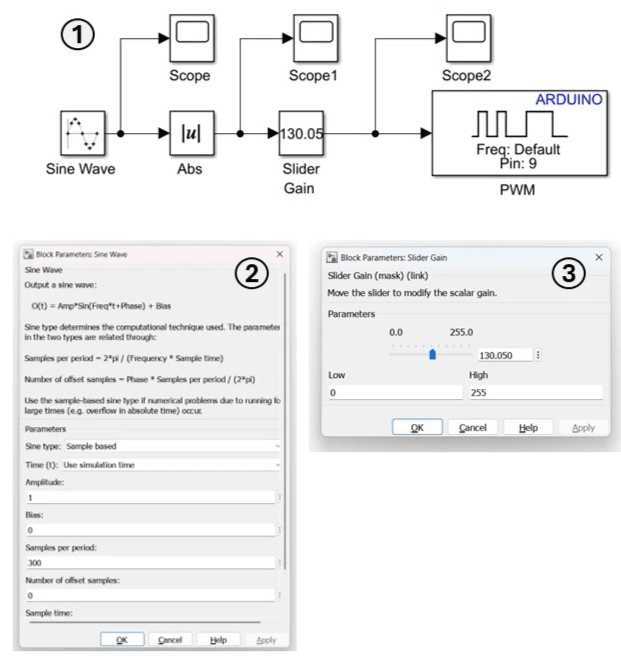
4. Simulink Set-Up and PWM Testing
In this part of the exercise, you will develop a Simulink model to control the Arduino PWM output and vary the LED brightness. A sine wave signal is used to smoothly vary the PWM duty cycle between 0 (OFF) and 255 (fully ON).
Simulink Model Construction Steps- Add a Sine Wave block (from Sources) and connect it to an Abs (absolute value) block (from Math Operations).
- Connect a Slider Gain block (from Math Operations), and set-up as following: The Slider Gain limits the maximum PWM value. For example, limiting the LED to approximately 2.3 corresponds to: 256 × 2.3 ≈ 117. For this exercise, set the upper limit to 255, corresponding to the full 5 output of the Arduino Uno.
- Add a PWM block (from Common in the Simulink Support Package for Arduino Hardware) and connect three Scope blocks (from Sinks) to observe relevant signals.
- Deploy the model using the same code-generation procedure as the previous exercise. Once deployed, observe the LED brightness variation and explore the effect of adjusting the Slider Gain.
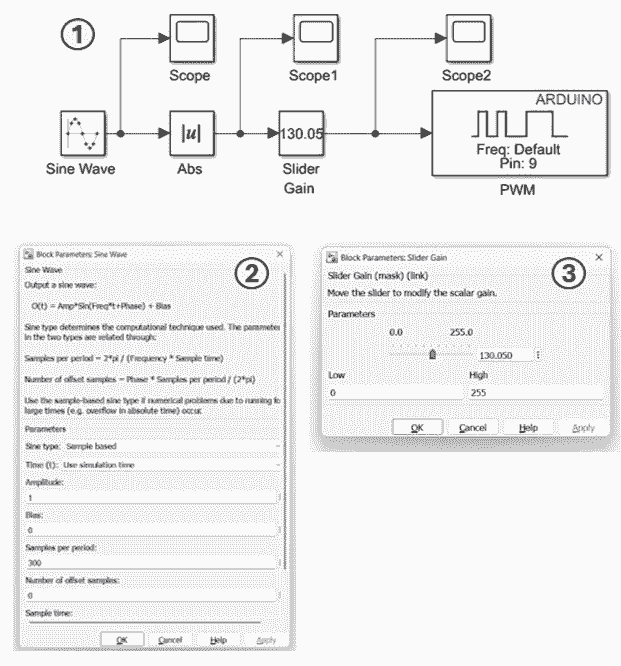
Key Properties to Modify
- Sine Wave (Sine type) → Set to Sample-based
- Sine Wave (Sample per period) → Set to Sample-based
- Sine Wave (Samples per period) → Set to 300
- Sine Wave (Sample time) → Set to 0.01 seconds
- Slider Gain (High) → Set to 255
All other properties may remain as their default values.
5. Additional Exercises
- Change PWM Signal Characteristics: Modify the input signal used to drive the PWM block (e.g. sine wave frequency or amplitude) and describe how these changes affect the rate and smoothness of the LED brightness variation.
- Modify PWM Range and Behaviour: Rewrite the PWM-related requirements in Section 2.0 by selecting new limits for the PWM output range (e.g. restricting the maximum brightness to less than 255). Update the Simulink model accordingly and observe the effect on the LED brightness when deployed to the Arduino. For this exercise, explore the use of the Saturation block within Simulink.
- Compare Digital and PWM Control: Using observations from this exercise and the previous LED (Digital) exercise, explain the difference between controlling an LED using a digital ON/OFF signal and using a PWM signal to vary brightness.
6. Concluding Remarks
This exercise has extended the previous digital LED control task by introducing Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) as a method for analogue-style control using adigital output. By varying the PWM duty cycle, you have demonstrated how LED brightness can be smoothly adjusted across multiple levels rather than simply switched ON or OFF.
Through the development and deployment of a Simulink model using a sine wave input, you have gained practical experience in applying model-based design to PWM control on embedded hardware. This reinforces key concepts including signal scaling, duty cycle control, and real-time execution using automatically generated code.
The LED (PWM) Exercise provides an important stepping stone toward more advanced embedded and control engineering applications, such as motor speed control, dimming systems, and closed-loop control. The principles applied here: clear requirements, correct hardware interfacing, and disciplined Simulink model configuration, will be reused and expanded in subsequent exercises.
Advancing automatic control engineering (ACE) education through global collaboration