Slide Potentiometer Exercise
1. Learning Outcomes
After completing this Section, you will be able to:
- Understand how to map the analogue input reading from the slide potentiometer to a suitable range and use it to control the LED brightness via PWM.
2. Hardware Set-Up
This exercise involves connecting an LED to a PWM output pin on the Arduino and controlling its brightness using the 10-bit analogue input from the slide potentiometer. The potentiometer provides 1024 possible input levels, which are mapped directly to 1024 brightness settings for the LED.
Required hardware for this exercise:
- Arduino Uno board (supported by Simulink)
- USB Cable Type A to B
- Breadboard
- LED
- 220 Ohm resistor
- Slide potentiometer
- 5 x male-male breadboard wires
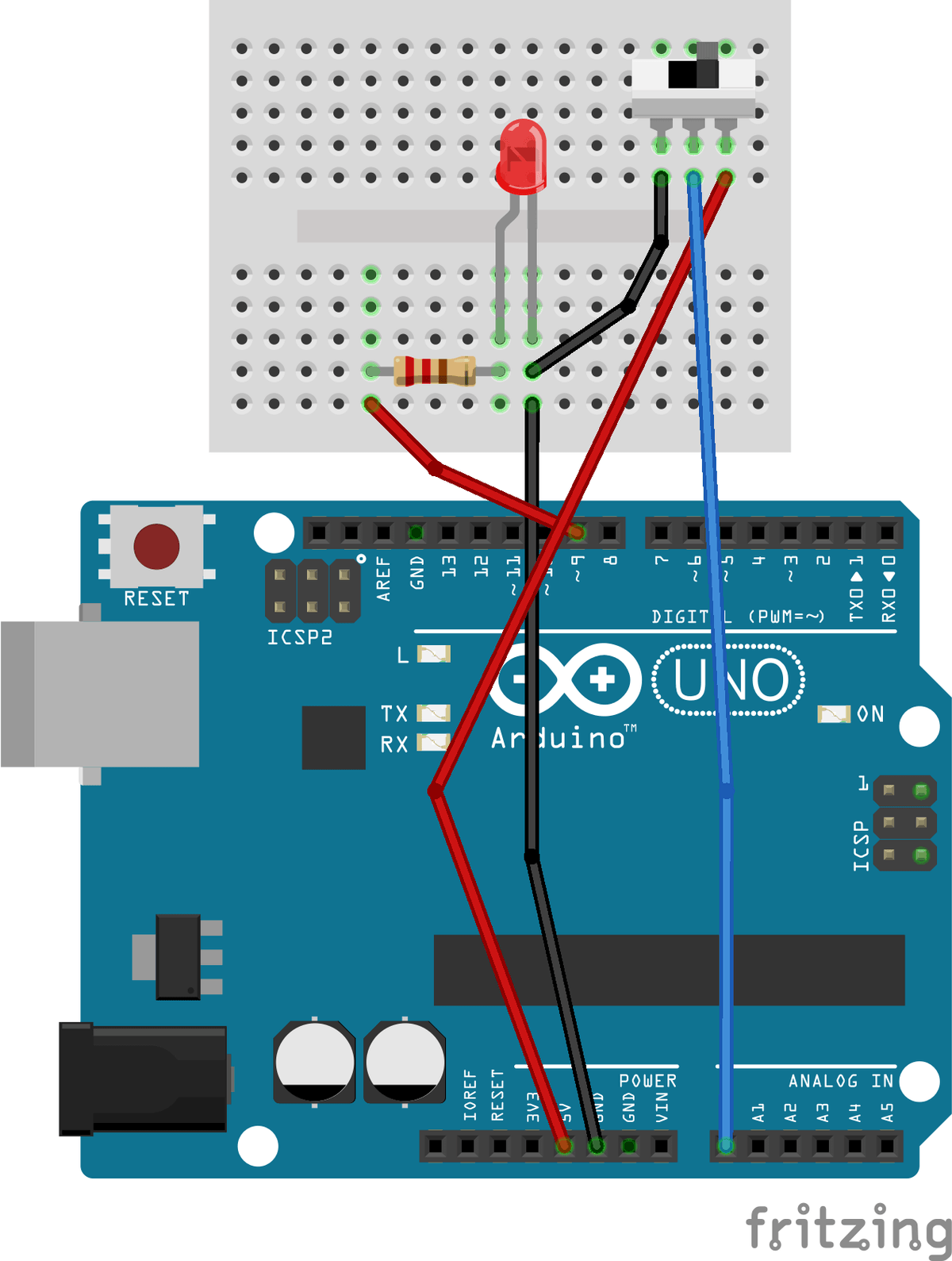
Set-up the hardware as shown and following these steps:
- Place the LED on the breadboard, connect its cathode to GND, and connect its anode through a 220 Ohm resistor to Pin 9.
- Place the slide potentiometer on the breadboard, connect its outer pins to 5V and GND, and connect its middle pin (wiper) to A0. Note that potentiometers do vary in type and it might be worth undertaking some background reading to understand exactly how the 3 pins map.
Download Now
Download the PDF version of the exercise
3. Simulink Setup and Testing
In this part of this initial exercise, you will develop a Simulink model to control the brightness of an LED using PWM, based on the analogue reading from a slide potentiometer, i.e., as the analogue reading of the slide potentiometer increases, so will the brightness of the LED. The steps for this exercise are very similar to those used for the LDR (light dependent resistor) exercise.
The steps to set up the model are as follows:
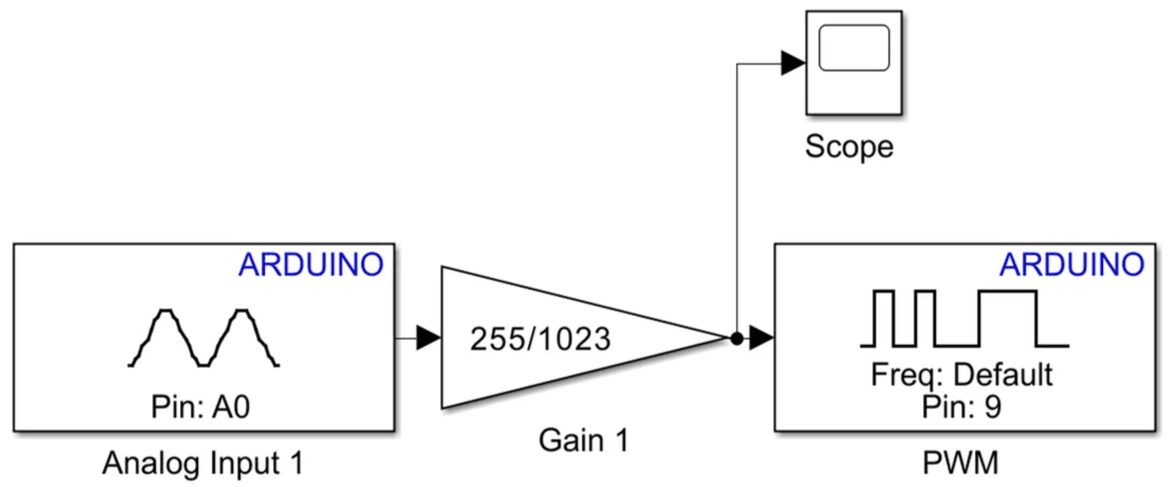
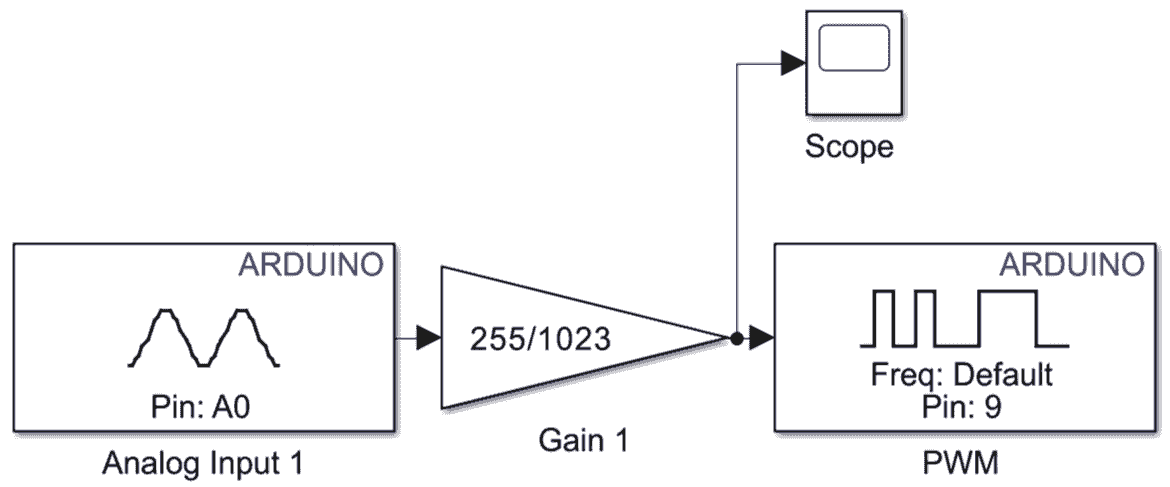
- Add an Analog Input block and changing the pin number of A0 and sample time to 0.01. This reads the sensor voltage and outputs a value between 0 and 1023.
- Insert a Gain block with value 255/1023. The gain block scales the ADC reading into the 0–255 range needed for PWM duty cycle.
- Connect the scaled signal to a PWM Output block and change the Pin to 9. The PWM block uses the 0–255 value to generate a proportional PWM signal on the Arduino.
- Connect one scope block to the signal after the gain block. This will enable the raw sensor reading to be viewed in real-time as the model runs, and also show the scaled PWM value, such that you can verify the conversion.
- Deploy the model to the Arduino. Once uploaded, adjust the slide potentiometer position to see the PWM output change, and the brightness of the LED.
Advancing automatic control engineering (ACE) education through global collaboration