Ultrasonic Sensor Exercise
1. Learning Outcomes
After completing this Section, you will be able to:
- Explain and demonstrate how to acquire distance measurements using a digital ultrasonic sensor.
- Implement a Last Good Value (LGV) logic filter to manage erroneous or intermittent readings from a digital sensor.
2. Hardware Set Up
The exercise involves connecting an HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor to an Arduino Uno to measure distance.
Note that while the ACE-Box (Base + Sense) can be used for all the exercises, it is not required and only the individual components are needed.
Required hardware for this exercise:
- Arduino Uno board (supported by Simulink)
- USB Cable Type A to B
- Breadboard
- Ultrasonic HC-SR04 sensor
- 4 x male-to-male wires
HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Specifications
- Distance measurement range: 0.02 to 4.00 meters
- Accuracy: ±0.003 meters
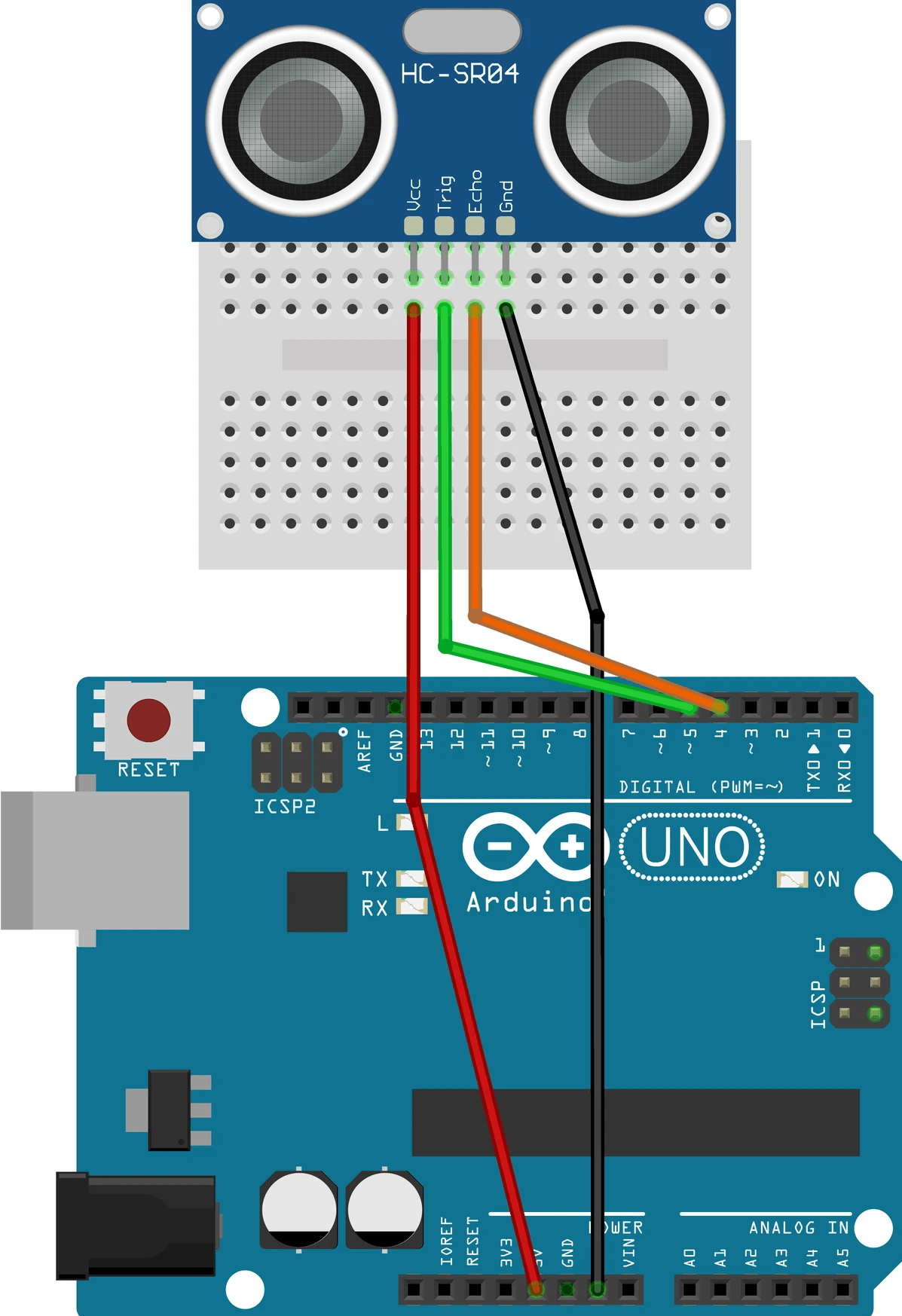
Set-up the hardware as shown and following these steps:
- Connect the ultrasonic sensor directly to the breadboard (as shown in the photo)
- Connect the 'Trig' signal to Pin 5 and the 'Echo' signal to Pin 4
- Connect the VCC terminal of the sensor to the 5V supply pin on the Arduino Uno.
- Connect Gnd terminal of the sensor to a GND pin on the Arduino Uno.
Download Now
Download the PDF version of the exercise
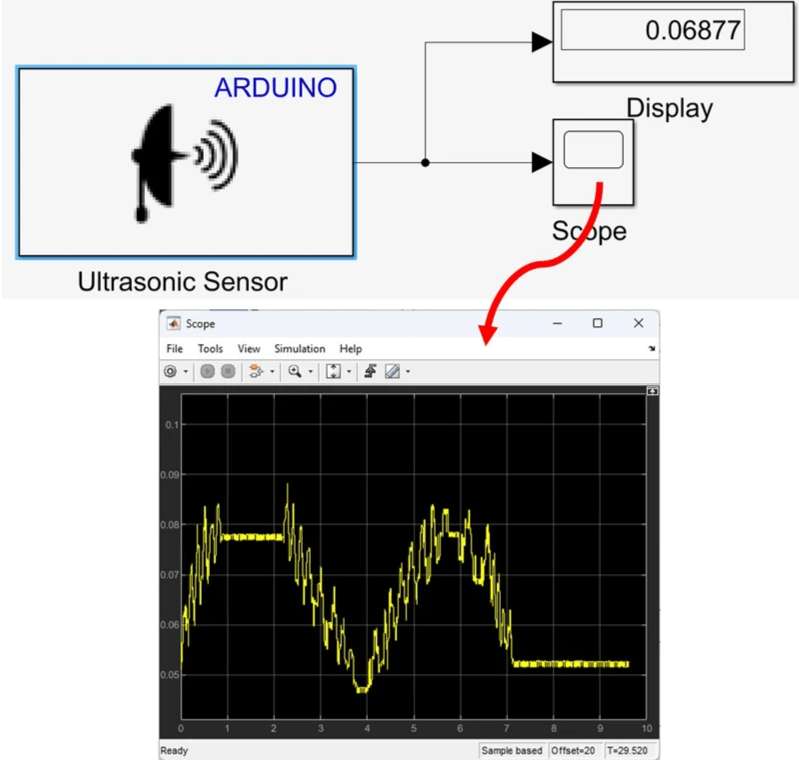
3. Simulink Set Up and Distance Measurement Testing
The complete Simulink diagram (i.e., algorithm design) for the hardware described above is given here. The "Ultrasonic Sensor" block can be found underthe Sensors tab in the Simulink Support Package for Arduino Hardware. Both the Display and Scope blocks are located under the Sinks tab in Simulink.
The steps to set up the model are as follows:
- Double-click the Ultrasonic Sensor block, then set the number of signal pins to 2.
- Define the trigger pin as 4 and the echo pin as 5.
- Select a sampling time/interval (e.g., 0.01 seconds). You should experiment with different values to determine the optimal setting.
- Run the Simulink model and observe the measured distance to the object ahead on the Scope (see the scope output illustrated in the Simulink illustration).
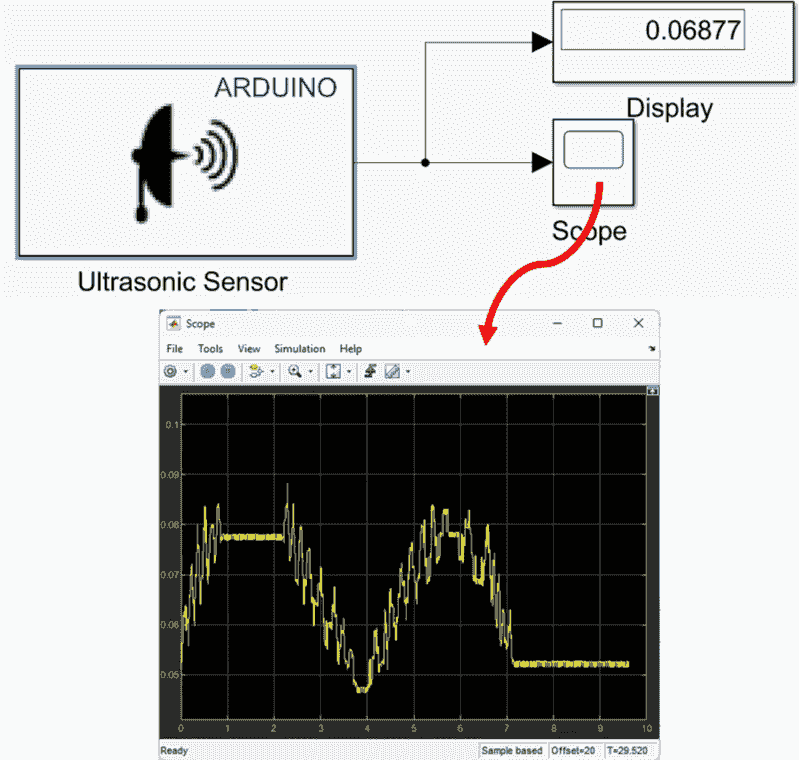
Key Properties to Modify
- Number of signal pins: 2
- Trigger pin: 4
- Echo pin: 5
- Sample time: 0.01
All other properties may remain as their default values.
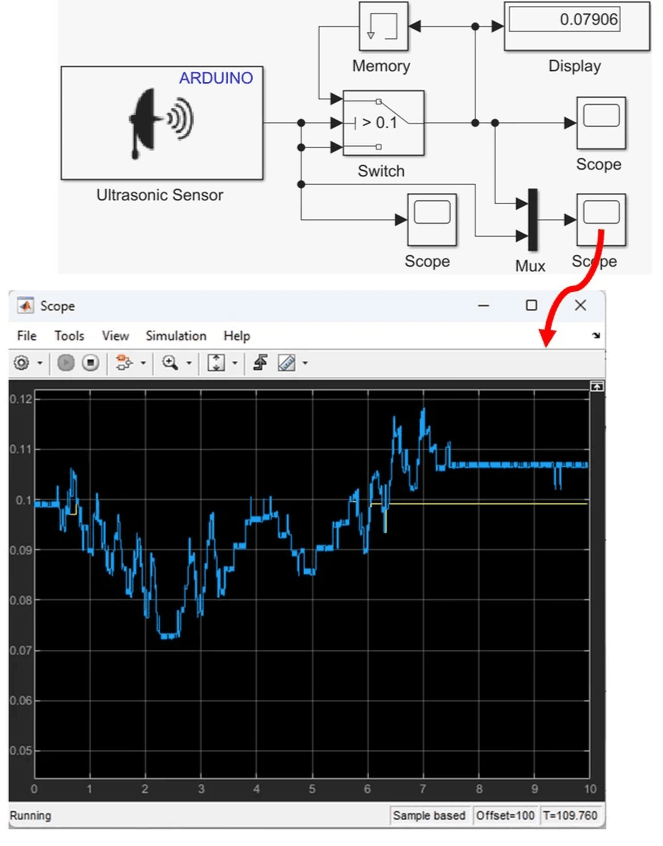
4. Last Good Value (LGV) Logic Filter and Testing
A last good value (LGV) logic filter is implemented. The LGV filter is used to maintain a valid output when the input signal becomes unreliable or invalid. It is particularly useful in situations where a sensor or input source might occasionally fail or produce noisy, erroneous data. The filter essentially "remembers" the last valid input value and continues to output this value until a new, valid reading is received. For example, in vehicles, if a sensor like an ultrasonic or radar sensor used for parking assistance fails or goes out of range temporarily, the LGV filter ensures the system still provides useful information based on the last good reading.
This setup can be configured to meet the operational requirements of the ultrasonic sensor, which has a measurement range of 0.02 to 4.00 meters. To implement this in Simulink use is made of the following blocks:
- The Switch block can be found under the Signal Routing section in Simulink. This block will be used to control the flow of data based on the sensor’s output.
- The Memory block, located under the 'Discrete' section, will store the last valid reading when the sensor output is below a certain threshold.
The blocks are the configured, with the set-up of the LGV filter logic as follows:
- Set up the flow of signals as displayed in the Simulink diagram
- Double-click the Switch block and set the Threshold to being greater than 0.1.
- Add a mux and scopes to allow for the signals to be viewed in real-time.
- Deploy the model and test the operation by operating the sensor within 0.1 meters and then beyond this.
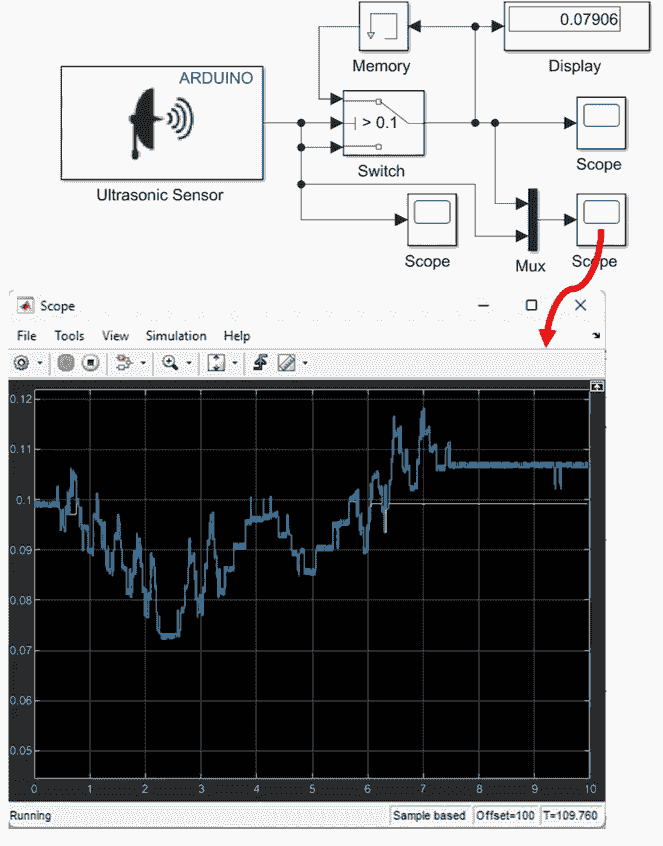
How it works
If the ultrasonic sensor's output value exceeds 0.1 meters, the Switch will output the current value, as illustrated in the scope (with the distance measurement exceeding 0.1 meters at approximately 6 seconds). However, if the sensor's output is below 0.1 meters, the Memory block will provide the last valid stored value below 0.1 meters.
Advancing automatic control engineering (ACE) education through global collaboration