LED (Digital) Exercise
1. Learning Outcomes
After completing this exercise, you will be able to:
- Understand the use of the Simulink Arduino support package for algorithm design applied to a simple digital circuit.
- Understand the function of the Arduino Uno digital Input/Output (I/O) pins through the implementation of an LED ON/OFF control task.
After completing this exercise, you are encouraged to review the learning outcomes and confirm that they have been met.
2. Requirements
The exercise has the following primary requirements:
- The Simulink model shall generate a digital output signal that turns an LED ON and OFF at a fixed, user-defined time interval of 0.5 (on) and 0.5 (off).
- The Simulink model shall use a sample-based pulse signal with a sample time of 0.1 to control an Arduino digital output pin.
- The Simulink model shall drive Arduino digital pin 9, outputting a logical LOW (0) to turn the LED OFF and a logical HIGH (255) to turn the LED ON.
- The Simulink model shall be deployable to an Arduino Uno using Simulink code generation and shall execute continuously in real-time (simulation stop time set to infinity).
3. Hardware Set-Up
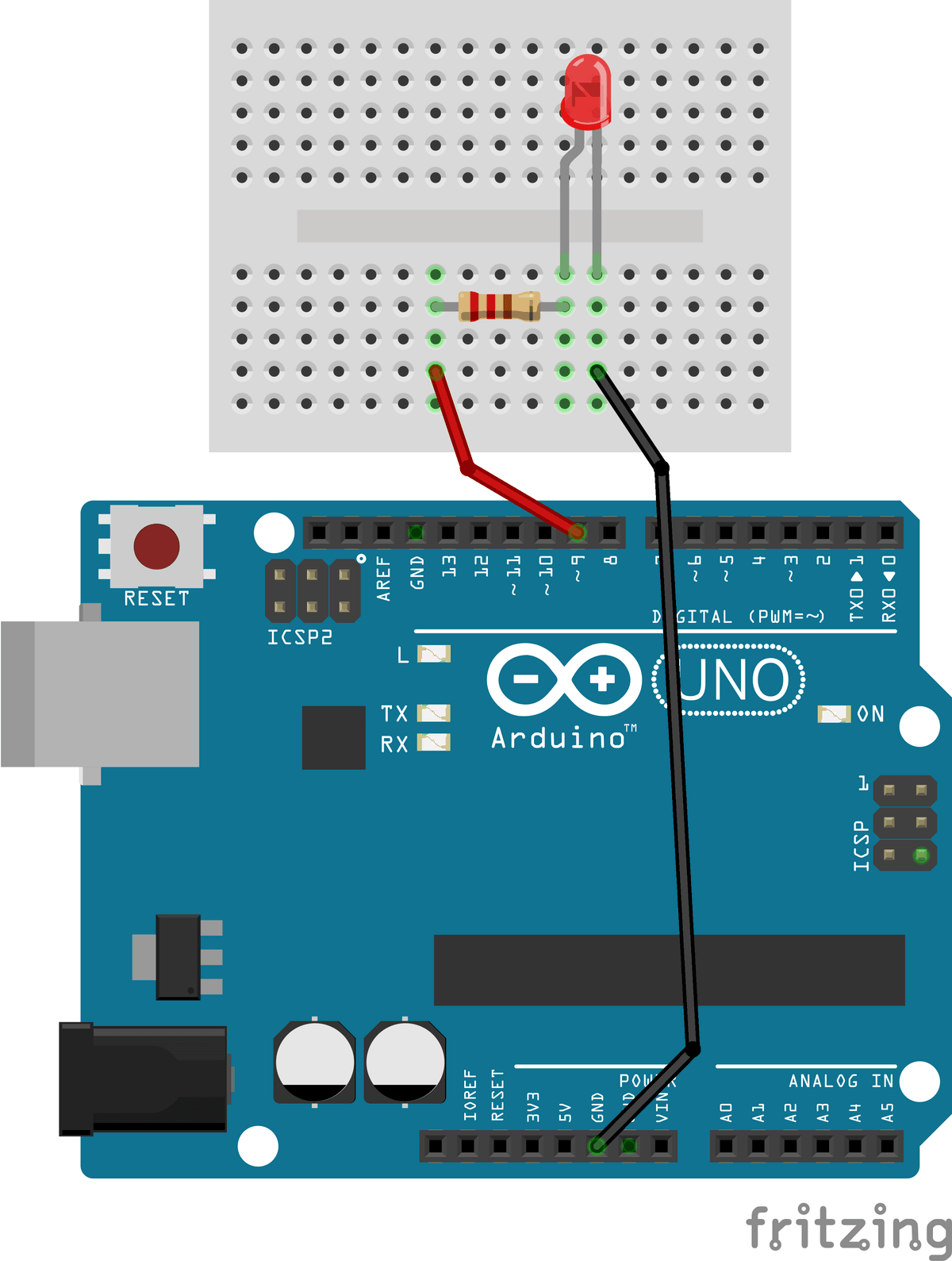
The exercise involves connecting an LED to a digital Arduino output pin and controlling its state by switching it on and off.
Note that while the ACE-Box can be used for all the exercises, it is not required and only the individual components are needed.
Required hardware for this exercise:- Arduino Uno board (supported by Simulink)
- USB Cable (Type A to Type B)
- Breadboard
- LED
- 220Ohm resistor
- 2 x male-to-male breadboard wires
HardwareAssembly Steps
- Connect digital pin 9 on the Arduino to a chosen column on the breadboard using a male-to-male jumper wire.
- Insert a 220 Ω resistor with one end in the same column as the wire from pin 9 and the other end in a different row.
- Insert the LED such that:
- The long leg (anode) is connected to the free end of the resistor.
- The short leg (cathode) is connected to an Arduino GND pin using a jumper wire.
4. Simulink Setup
In this part of the exercise, you will develop a Simulink model to control the Arduino digital output pin and turn the LED ON and OFF. A Pulse Generator block is used to alternate the output between 0 (OFF) and 255 (ON).
Simulink Model Construction Steps
- From Simulink → Sources, add a Pulse Generator block to the model.
- From Simulink Support Package for Arduino Hardware → Common, add a Digital Output block.
- Connect the output of the Pulse Generator block to the input of the Digital Output block.
- Open the Pulse Generator block parameters and configure: Pulse Type: Sample based and Sample time: 0.1 seconds.
- Open the Digital Output block parameters and set: Pin number: 9.
- From Simulink → Sinks, add a Scope block.
- Branch the signal from the Pulse Generator output and connect it to the Scope input to monitor the generated waveform.
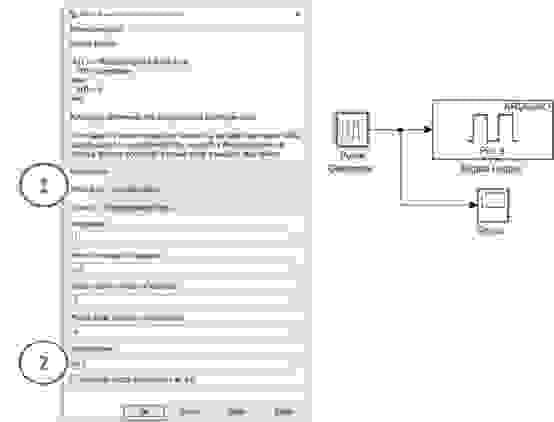
Key Properties to Modify
- Pulse type → Set to Sample-based
- Sample time → Set to 0.1 seconds
All other properties may remain as their default values.
5. Running Simulink Code Generation
In this part of the exercise, you will configure and run a Simulink model to perform code generation on a supported Arduino Uno board. Using the following steps and as shown in the illustration, undertake the following:
- Connect the Arduino Uno to your computer using a USB cable.
- In your Simulink window, open Model Settings by selecting Modelling → Model Settings. This will bring up the Configuration Parameters dialog.
- From the left-hand menu, select Hardware Implementation. Under Hardware board, choose Arduino Uno from the list, then click Apply and OK. Note that other boards can be used beyond that of the Arduino Uno.
- A new Hardware tab will now appear in Simulink. (Ensure your Simulink model is already developed before reaching this step.)
- Important: make sure MATLAB is operating/saving in a suitable working directory before clicking ‘Run’
- Confirm that the Arduino Uno is displayed, change the simulation stop time to inf (infinity), and then click Monitor & Tune. The Simulink model will now be deployed to the Arduino, compiled into C code, and executed on the hardware.
⚠️If you encounter any errors, click the link below for troubleshooting
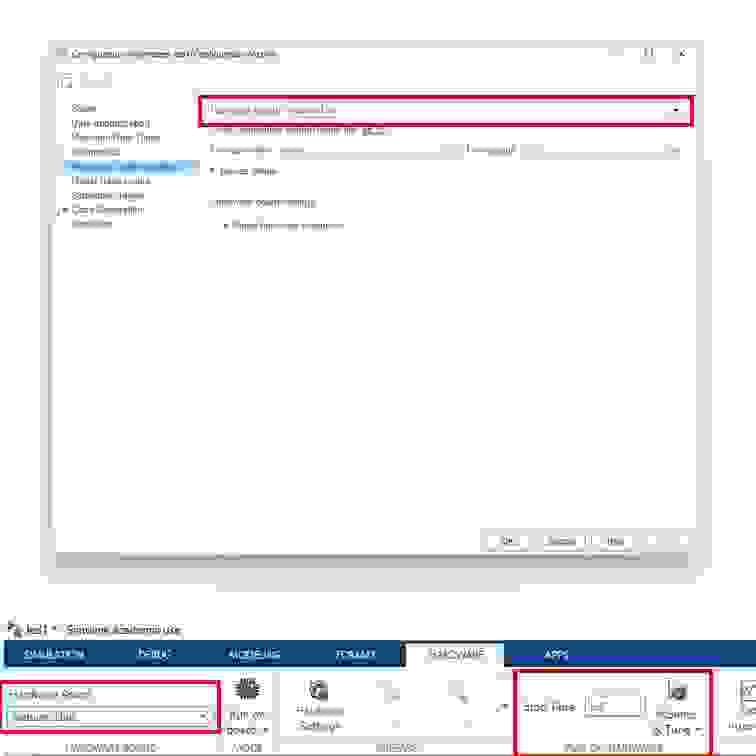
Key Properties from Above:
- Modeling settings
- Selected hardware board → Arduino Uno
- Simulation stop time → inf
- Monitor & Tune configuration
6. Exercises
- Modify Timing Requirements: Rewrite the timing-related requirements defined in Section 2.0 (i.e., the LED ON/OFF period and the sample time) using new, user-defined values. Update the Simulink model accordingly and verify that the deployed system operates with the revised timing parameters.
- Out-of-Sequence LED Control: Extend the system by adding a second LED connected to a different Arduino digital output pin.
- First, write a new set of requirements specifying out-of sequence (phase-shifted) LED behaviour.
- Then, implement and deploy the Simulink model to demonstrate asynchronous operation of the two LEDs.
7. Concluding Remarks
This exercise has demonstrated the complete workflow forimplementing a simple digital control task using Simulink and an Arduino Uno, from defining requirements through to real-time execution on hardware. By developing, configuring, and deploying a Simulink model to control an LED, you have gained practical experience in linking model-based design with embedded hardware implementation.The exercise reinforces key concepts including digital input/output(I/O) operation, timing through sample-based signals, and automatic C-code generation using the Simulink Arduino support package. Importantly, it illustrates how abstract control logic developed in Simulink can be translated directly into executable behaviour on a physical system without manual
programming.This LED (Digital) Exercise serves as a foundationalbuilding block for more advanced tasks involving sensors, actuators, and closed-loop control. The same principles applied here: clear requirements, correct hardware interfacing, and disciplined model configuration. This will
extend naturally to more complex embedded and control engineering applications introduced in subsequent exercises.
Advancing automatic control engineering (ACE) education through global collaboration





