
- Start Here!
- ACE-Box: Launch: 21/01/26
- Start Here!
- 1. Comprehend
- 2. Operate
- 3. Refine
- 4. Engineer
- …
- Start Here!
- ACE-Box: Launch: 21/01/26
- Start Here!
- 1. Comprehend
- 2. Operate
- 3. Refine
- 4. Engineer
- Start Here!
- ACE-Box: Launch: 21/01/26
- Start Here!
- 1. Comprehend
- 2. Operate
- 3. Refine
- 4. Engineer
- …
- Start Here!
- ACE-Box: Launch: 21/01/26
- Start Here!
- 1. Comprehend
- 2. Operate
- 3. Refine
- 4. Engineer
Hardware Set-Up
The exercise involves connecting an LED to a digital Arduino output pin and controlling its state by switching it on and off.
This is the same set-up as used in the previous exercise.
Note that while the ACE-Box can be used for all the exercises, it is not required and only the individual components are needed.
Required hardware for this exercise:- Arduino Uno board (supported by Simulink)
- USB Cable Type A to B
- Breadboard
- LED
- 220Ohm resistor
- 2 x male-male breadboard wires
Set-up the hardware as shown and following these steps:
- Attach one end of the 220Ohm resistor to output pin 9 on the Arduino board, using the small breadboard and male-male breadboard wires
- Attach the long leg (positive) of the LED to the resistor
Exercise Algorithm Design – LED Varying Brightness
In this part of the exercise, you will develop a Simulink model to control the Arduino PWM output (1). The PWM signal will be set to values between 0 (off) and 255 (fully on), which will adjust the LED brightness across its full range.
The steps to set up the model are as follows:
- Use a Sine Wave block (from Sources) as the input and connect it to an Abs (absolute value) block (from Math Operations), as shown in (2).
- Connect a Slider Gain block (from Math Operations). You can specify the lower (Low) and upper (High) limits of the gain to constrain the output voltage. For example, to limit the voltage to 2.3 V: 256 × 2.3 = 117.76 ≈ 117. In this case, the upper limit (High) for the saturation block would be set to 117. However, for this exercise, set the upper limit to 255 (equivalent to 5 V on the Arduino Uno) (3).
- Add a PWM block (from Common in the Simulink Support Package for Arduino Hardware) and connect three Scopes (from Sinks).
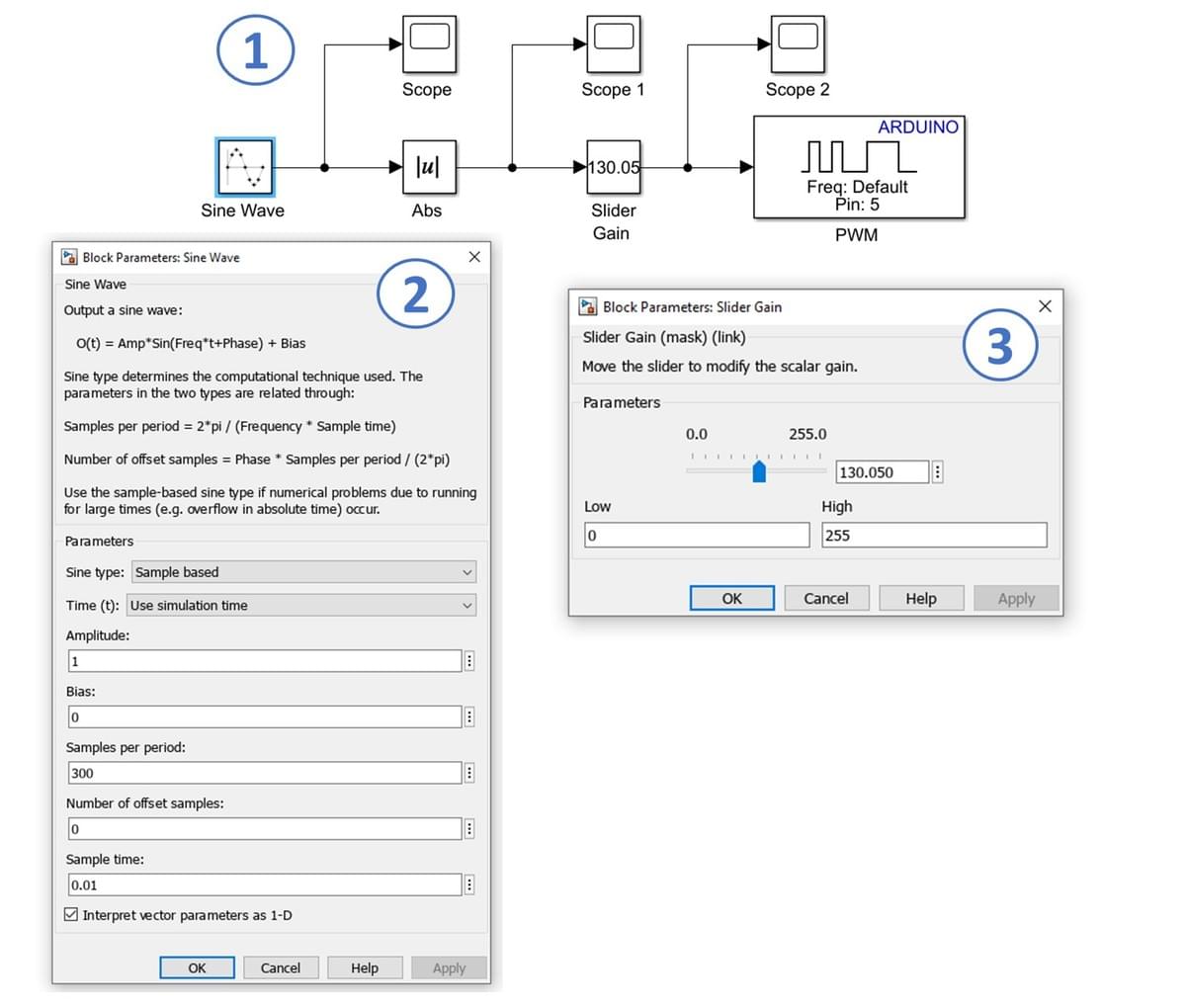
Key Properties to Modify
- Sine Wave (Sine type) → Set to Sample-based
- Sine Wave (Sample per period) → Set to Sample-based
- Sine Wave (Sample time) → Set to 0.01 seconds
- Slider Gain (High) → Set to 255
All other properties may remain as their default values.
Running Exercise 1 (Code Generation)
This is the same set-up as used in the previous exercise.
In this part of the exercise, you will configure and run a Simulink model on the supported Arduino Uno board. Using the following steps and as stown in the illustration, undertake the following:
- Connect the Arduino Uno to your computer using a USB cable.
- In your Simulink window, open Model Settings by selecting Modeling → Model Settings. This will bring up the Configuration Parameters dialog (1).
- From the left-hand menu, select Hardware Implementation. Under Hardware board, choose Arduino Uno from the list, then click Apply and OK (1). Note that other boards can be used beyond that of the Ardruino Uno.
- A new Hardware tab will now appear in Simulink. (Ensure your Simulink model is already developed before reaching this step.)
- Important: make sure MATLAB is operating/saving in a suitable working directory before clicking ‘Run’
- Confirm that the Arduino Uno is displayed (2), change the simulation stop time to inf (infinity) (3), and then click Monitor & Tune (4). The Simulink model will now be deployed to the Arduino, compiled into C code, and executed on the hardware.
⚠️If you encounter any errors, click the link below for troubleshooting
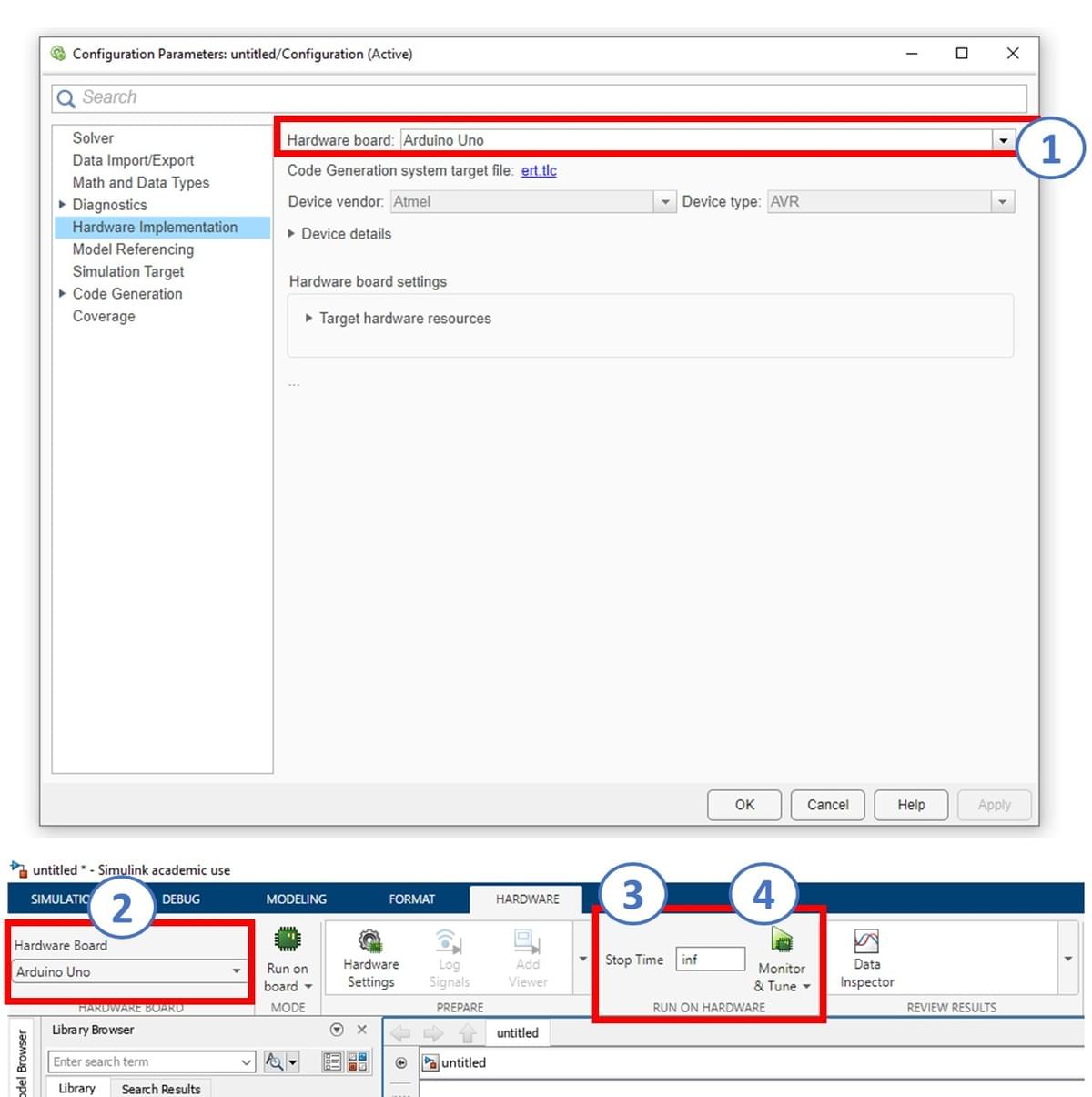
Key Properties to Review/Adjust
- Modeling settings
- Selected hardware board → Arduino Uno
- Simulation stop time → inf
- Monitor & Tune configuration
Advancing control engineering education through global collaboration




